The heat pump basics
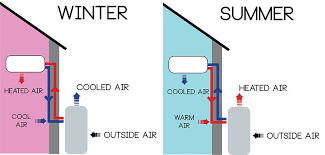
Put simply, a heat pump is a gadget that is utilized to move warm from one area to an additional. It can be used for both home heating well as cooling down functions. It can either take heat from the inside as well as eject it outside, cooling, or it can take warmth from outside as well as inject it inside, heating.
Currently, there are several means whereby this feature can be attained; let’s undergo that carefully:
Heat pumps efficiency is more than electric resistance heating units. Yet there is one catch. This efficiency reduces as the temperature slope or the difference in the outdoor, as well as indoor temperatures, begin to increase. Various light companies can assist you in estimating how much electricity your heat pump will use so that you know how much you’ll be spending on your power bill.
Using the term “heat pump” can confuse lots of people right into believing that these devices can just warm an indoor space as well as not cool it. But as we have specified earlier on, they can do both jobs, often through a solitary home appliance. This is attained via the use of a “turning around shutoff” in the case of AC. Through this device, the evaporator and condenser coils can be interchanged, i.e., the condenser can end up being the evaporator, as well as the evaporator can end up being the condenser, as called for.
To read about a guide to heat pumps and finding the best contractor, please follow the link.
How Do Warmth Pumps Function?
How a heat pump works is by relocating a fluid referred to as a cooling agent throughout different parts referred to as the compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion shutoff. The refrigerant works as the key tool through which the warmth is got rid of or added to space. It can absorb warmth from its atmosphere as well as cool it when combined with various other components such as condensers or evaporators. The very same procedure can be turned around to obtain a heating plan.
The cooling agent goes through the expansion valve, and it converts the formerly fluid refrigerant right into a gas. Throughout this expansion, the refrigerant cools. It is after that run via many coils inside the evaporator, and are blown using a fan. Cold air is hence injected right into the area, and warmth is absorbed by the refrigerant, which turns into a warm gas.
It is after that going through the compressor, where it is compressed and converted into a high-temperature high-pressure gas. The refrigerant is presented via a network of coils inside the condenser, as well as blown by using fans to get rid of the stored heat by ejecting it right into the outdoor environment. The cooling agent, which is a liquid now, is cycled once more via the same procedure to continue obtaining cold air.
To learn more about residential heat pumps, please click on the link.
